library(dplyr) # AND
library(tidyr)
# OR (recommended here)
library(tidyverse)Data wrangling - Introduction
Manipulating rows and columns
R Workshop
Tuesday, 11 February 2025
Introduction
Data munging
- Preparing data is the most time consuming part of data analysis.
- Individual steps might look easy.
- Essential part of understanding the data you’re working with.
- Additional data preparation before modeling is impossible to avoid.
At a glance
dplyr is a tool box for working with data in tibbles, offering a unified language for operations scattered through base R.

Key operations
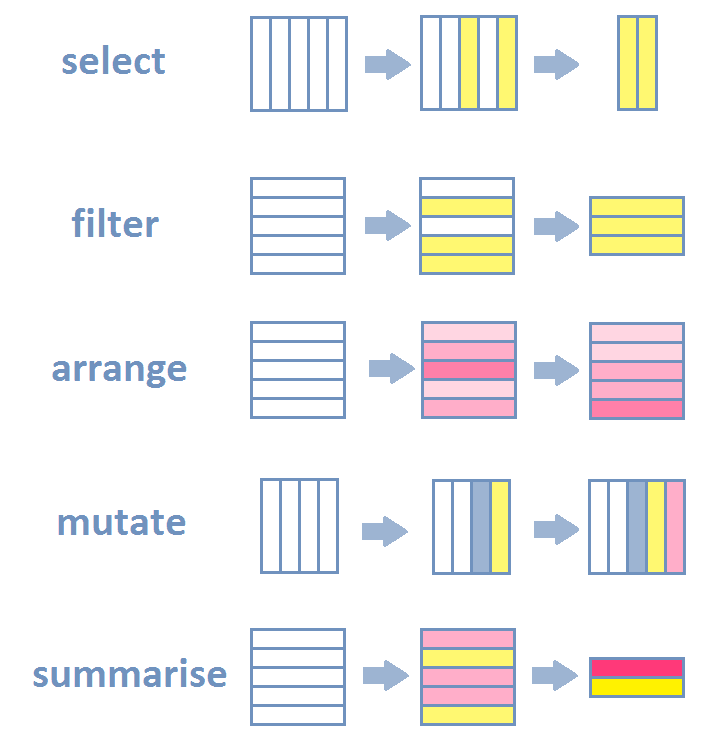
This lecture
Example data
Van ’t Veer, Anna; Sleegers, Willem, 2019, “Psychology data from an exploration of the effect of anticipatory stress on disgust vs. non-disgust related moral judgments”. Journal of Open Psychology Data.
- Data is not really tidy.
- Typical data you might see in the wild.
Learning objectives
Learn the grammar to operate on rows and columns of a table
Selection and manipulation of
- observations,
- variables and
- values.
Grouping and summarizing
Joining and intersecting tibbles
Pivoting column headers and variables
Key operations

dplyr Introduction: Cheat sheets
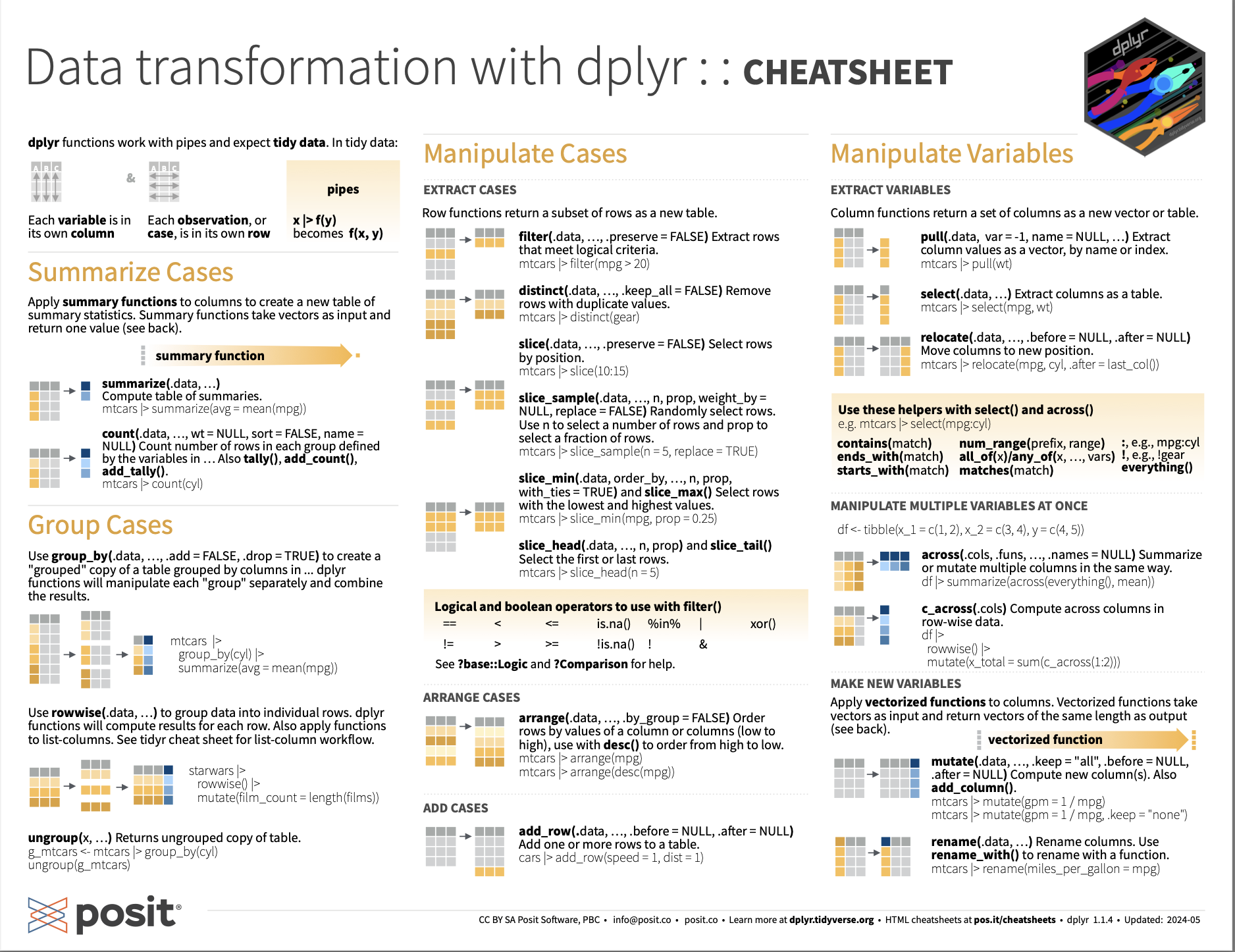
Using the dplyr package
Do not use these packages!
dplyrsupersedes previous packages from Hadley Wickham.reshapereshape2plyr
- All functionality can be found in
dplyrortidyr.
dplyr current version is 1.1.4
dplyrhas seen many changes.Watch out for deprecated examples on Stack overflow!
Code will break sooner or later (you might get lucky)
But handled with clear lifecycle stages now
Changes are generally introduced to simplify operations.
Loading dplyr
Inspecting tibbles
Inspect tibbles with glimpse()
Column-wise description
Shows some values and the type of each column.
The Environment tab in RStudio tab does it too.
Clicking object judgments triggers View().
Similar to the utils::str() function
Rows: 188
Columns: 158
$ start_date <date> 2014-03-11, …
$ end_date <date> 2014-03-11, …
$ finished <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ condition <chr> "control", "s…
$ subject <dbl> 2, 1, 3, 4, 7…
$ gender <chr> "female", "fe…
$ age <dbl> 24, 19, 19, 2…
$ mood_pre <dbl> 81, 59, 22, 5…
$ mood_post <dbl> NA, 42, 60, 6…
$ STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl> 2, 3, 3, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl> 2, 1, 3, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 2…
$ STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl> 2, 2, 2, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl> 2, 3, 3, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl> 1, 2, 2, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl> 1, 2, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl> 1, 2, 4, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl> 1, 3, 4, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_7 <dbl> 1, 1, 2, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_3_1 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 1…
$ STAI_pre_3_2 <dbl> 2, 3, 3, 3, 2…
$ STAI_pre_3_3 <dbl> 2, 3, 2, 2, 2…
$ STAI_pre_3_4 <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_3_5 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_3_6 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_post_1_1 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_1_2 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_1_3 <dbl> NA, 3, 2, 1, …
$ STAI_post_1_4 <dbl> NA, 3, 2, 1, …
$ STAI_post_1_5 <dbl> NA, 2, 2, 2, …
$ STAI_post_1_6 <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_1_7 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_1 <dbl> NA, 2, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_2_2 <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_3 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_2_4 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_2_5 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_6 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_7 <dbl> NA, 1, 1, 2, …
$ STAI_post_3_1 <dbl> NA, 2, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_3_2 <dbl> NA, 2, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_3_3 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_3_4 <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_3_5 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 3, …
$ STAI_post_3_6 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ moral_dilemma_dog <dbl> 9, 9, 8, 8, 3…
$ moral_dilemma_wallet <dbl> 9, 9, 7, 4, 9…
$ moral_dilemma_plane <dbl> 8, 9, 8, 8, 9…
$ moral_dilemma_resume <dbl> 7, 8, 5, 6, 5…
$ moral_dilemma_kitten <dbl> 9, 9, 8, 9, 5…
$ moral_dilemma_trolley <dbl> 5, 3, 5, 2, 4…
$ moral_dilemma_control <dbl> 9, 2, 9, 8, 8…
$ presentation_experience <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 2, …
$ presentation_unpleasant <dbl> NA, 63, 68, 3…
$ presentation_fun <dbl> NA, 58, 26, 5…
$ presentation_challenge <dbl> NA, 58, 65, 8…
$ PBC_1 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_2 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_3 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_4 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_5 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_1 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_2 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_3 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_4 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_5 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_6 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_7 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_8 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_9 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_10 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_11 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_12 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_13 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_14 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_15 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_16 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_17 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_18 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_19 <dbl> 1, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_20 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_21 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_22 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_23 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_24 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_25 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_26 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_27 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_28 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_29 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_30 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_31 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_32 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_33 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_34 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_35 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_36 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_37 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_38 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_39 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_40 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_1 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_2 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_3 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_4 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_5 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_6 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_7 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_8 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_9 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_10 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_11 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_12 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_13 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_14 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_15 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_16 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_1 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_2 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_3 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_4 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_5 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_6 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_7 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_8 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_9 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_10 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_11 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_12 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_13 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_14 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_15 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_16 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ STAI_pre <dbl> 32, 49, 65, 4…
$ STAI_post <dbl> NA, 51, 41, 3…
$ MAIA_noticing <dbl> 14, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_not_distracting <dbl> 6, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_not_worrying <dbl> 11, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_attention_regulation <dbl> 27, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_emotional_awareness <dbl> 20, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_self_regulation <dbl> 16, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_body_listening <dbl> 10, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_trusting <dbl> 12, NA, NA, N…
$ PBC <dbl> 21, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_rational_ability <dbl> 38, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_rational_engagement <dbl> 38, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_experiental_ability <dbl> 36, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_experiental_engagement <dbl> 39, NA, NA, N…
$ moral_judgment <dbl> 8.000000, 7.0…
$ moral_judgment_disgust <dbl> 8.666667, 9.0…
$ moral_judgment_non_disgust <dbl> 7.000000, 6.6…
$ presentation_evaluation <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 4, …
$ logbook <chr> NA, NA, NA, N…
$ exclude <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0…Selecting columns
select(tibble, column1, ...)
# A tibble: 188 × 3
gender age condition
<chr> <dbl> <chr>
1 female 24 control
2 female 19 stress
3 female 19 stress
4 female 22 stress
5 female 22 control
6 female 22 stress
7 female 18 control
8 male 20 control
9 female 21 stress
10 female 19 stress
# ℹ 178 more rowsNon-standard evaluation
Note the absence of quotes around column names!
Warning
The biomaRt package of Bioconductor (amongst others) provides a select() function. If loaded, we need to address the dplyr-package using ::!
Reminder tidyselect
Helper function
To select columns with names that:
contains()- a stringstarts_with()- a stringends_with()- a stringany_of()- any names in a character vectorc("col_name")all_of()- all names in a character vectorc("col_name")matches()- using regular expressionseverything()- all remaining columnslast_col()- last column
Avoid selecting columns by index!
To ensure reproducibility select columns by name
# A tibble: 188 × 10
moral_dilemma_dog moral_dilemma_wallet
<dbl> <dbl>
1 9 9
2 9 9
3 8 7
4 8 4
5 3 9
6 9 9
7 9 5
8 9 4
9 6 9
10 6 8
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 8 more variables: moral_dilemma_plane <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_resume <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_kitten <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_trolley <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_control <dbl>,
# moral_judgment <dbl>, …Combining helpers
Remark
Helpers are found in several functions, e.g. across().
Use Boolean logic for combining
selection1 & selection2 - vars found in both selections
selection1 | selection2 - vars found in either of selections
# A tibble: 188 × 9
start_date end_date moral_dilemma_dog
<date> <date> <dbl>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 9
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 9
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 8
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 8
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 3
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 9
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 9
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 9
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 6
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 6
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: moral_dilemma_wallet <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_plane <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_resume <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_kitten <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_trolley <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_control <dbl>Selecting with quoted names
Selecting columns to omit
! Negative selection
Drop columns by negating their names with !
Works with the tidyselect helper functions.
# A tibble: 188 × 71
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 67 more variables: subject <dbl>, age <dbl>,
# mood_pre <dbl>, mood_post <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_dog <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_wallet <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_plane <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_resume <dbl>, …Column output depends on helper function order
# A tibble: 188 × 4
mood_pre mood_post start_date end_date
<dbl> <dbl> <date> <date>
1 81 NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
2 59 42 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
3 22 60 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
4 53 68 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
5 48 NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
6 73 73 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
7 NA NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
8 100 NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
9 67 74 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
10 30 68 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
# ℹ 178 more rows# A tibble: 188 × 4
start_date end_date mood_pre mood_post
<date> <date> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 81 NA
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 59 42
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 22 60
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 53 68
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 48 NA
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 73 73
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 NA NA
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 100 NA
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 67 74
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 30 68
# ℹ 178 more rowsTip
Helpers are evaluated left to right
relocate()
.beforeand.afterfor fine placement. Works also withmutate()
# A tibble: 188 × 158
start_date STAI_pre_1_1 STAI_pre_1_2
<date> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2014-03-11 2 1
2 2014-03-11 3 2
3 2014-03-11 4 3
4 2014-03-11 2 2
5 2014-03-11 1 1
6 2014-03-11 2 2
7 2014-03-11 2 2
8 2014-03-11 1 1
9 2014-03-11 2 2
10 2014-03-11 4 2
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 155 more variables: STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl>, …
Filtering for rows: filter()
Let’s take a look at all the data that was excluded. The column exclude is coded as \(0=include\) and \(1=exclude\).
# A tibble: 3 × 158
start_date end_date finished condition subject
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 28
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 32
3 2014-07-11 2014-07-11 1 stress 181
# ℹ 153 more variables: gender <chr>, age <dbl>,
# mood_pre <dbl>, mood_post <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>, …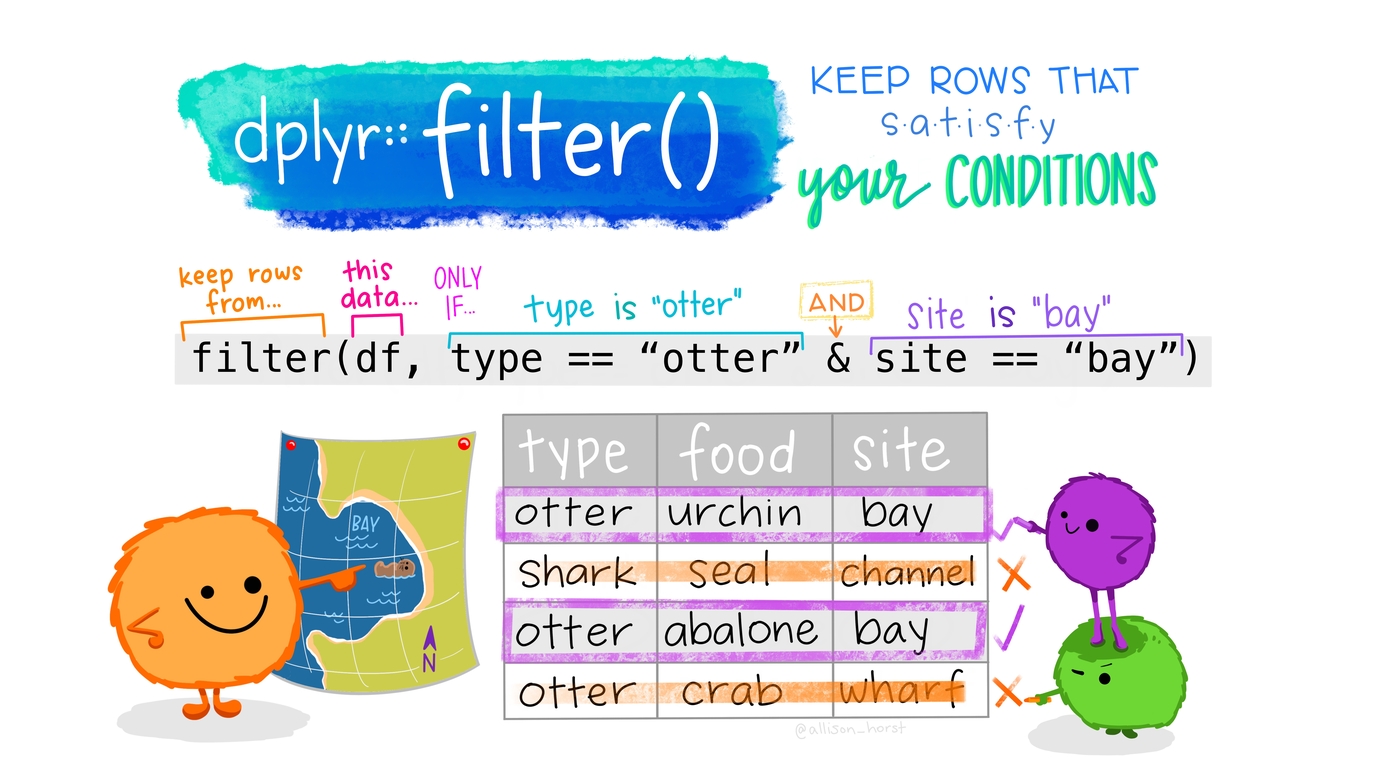
Filtering rows
Multiple conditions: AND
&to combine conditions with AND- Filter for females older than 20.
# A tibble: 34 × 158
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
# ℹ 24 more rows
# ℹ 154 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>,
# mood_post <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …Multiple conditions: OR
- vertical bar (
|) separated conditions are combined with OR. - Filter females or age > 20 (so males too)
# A tibble: 164 × 158
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
# ℹ 154 more rows
# ℹ 154 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>,
# mood_post <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …Filtering out rows
Row vs column selection
filter()acts on rowsselect()acts on columns
- Remove excluded participants
- Combine with
relocate()to placemoodcolumns first
# A tibble: 185 × 158
mood_pre mood_post start_date end_date
<dbl> <dbl> <date> <date>
1 81 NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
2 59 42 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
3 22 60 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
4 53 68 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
5 48 NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
6 73 73 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
7 NA NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
8 100 NA 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
9 67 74 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
10 30 68 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
# ℹ 175 more rows
# ℹ 154 more variables: finished <dbl>,
# condition <chr>, subject <dbl>, gender <chr>,
# age <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …Filter rows, helper between()
# A tibble: 64 × 4
age gender condition mood_pre
<dbl> <chr> <chr> <dbl>
1 19 female stress 59
2 22 female stress 53
3 22 female control 48
4 19 female stress 55
5 18 female stress 53
6 19 female control 59
7 19 female stress 60
8 22 male stress 53
9 18 male control 50
10 19 female stress 58
# ℹ 54 more rowsSet operations with filter()
date_choice <- as.Date(c("2014-03-11", "2014-05-11"))
judgments |>
filter(is.element(
start_date, date_choice)) |>
select(start_date:age)# A tibble: 79 × 7
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
# ℹ 69 more rows
# ℹ 3 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>Not efficient for large data sets
For larger operations use filtering joins such as semi_join().
# A tibble: 79 × 7
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
# ℹ 69 more rows
# ℹ 3 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>Filter out rows that are unique: distinct()
Do we have different start / end dates?
# A tibble: 188 × 2
start_date end_date
<date> <date>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
# ℹ 178 more rowsToo many identical rows
Use distinct() to remove duplicated rows:
# A tibble: 5 × 2
start_date end_date
<date> <date>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
2 2014-04-11 2014-04-11
3 2014-05-11 2014-05-11
4 2014-06-11 2014-06-11
5 2014-07-11 2014-07-11- Also possible (except columns order):
Sort columns: arrange()
A nested sorting example
- Sort by
age - Within each group of
age, sort bymood_post
Reverse sort columns
- Use
arrange()with the helper functiondesc() - For example, oldest participant first
Verbs to inspect data
Summary
glimpse()to get an overview of each column’s contentselect()to pick and/or omit columns- helper functions
relocate()re-arrange columns orderfilter()to subset- AND/OR conditions (
,,|)
- AND/OR conditions (
arrange()to sort- combine with
desc()to reverse the sorting
- combine with

Your turn!
Exercises
Use
glimpse()to identify columns and column types injudgments.Select all columns that refer to the STAI questionnaire.
Retrieve all subjects younger than 20 which are in the stress group. The column for the group is
condition.Arrange all observations by
STAI_preso that the subject with the lowest score is on top. What is the subject in question?
05:00
Solution
Rows: 188
Columns: 158
$ start_date <date> 2014-03-11, …
$ end_date <date> 2014-03-11, …
$ finished <dbl> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1…
$ condition <chr> "control", "s…
$ subject <dbl> 2, 1, 3, 4, 7…
$ gender <chr> "female", "fe…
$ age <dbl> 24, 19, 19, 2…
$ mood_pre <dbl> 81, 59, 22, 5…
$ mood_post <dbl> NA, 42, 60, 6…
$ STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl> 2, 3, 3, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl> 2, 1, 3, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 2…
$ STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl> 2, 2, 2, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl> 2, 3, 3, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl> 1, 2, 2, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl> 1, 2, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl> 1, 2, 4, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl> 1, 3, 4, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_2_7 <dbl> 1, 1, 2, 2, 1…
$ STAI_pre_3_1 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 1…
$ STAI_pre_3_2 <dbl> 2, 3, 3, 3, 2…
$ STAI_pre_3_3 <dbl> 2, 3, 2, 2, 2…
$ STAI_pre_3_4 <dbl> 1, 2, 3, 1, 1…
$ STAI_pre_3_5 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_pre_3_6 <dbl> 2, 3, 4, 3, 3…
$ STAI_post_1_1 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_1_2 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_1_3 <dbl> NA, 3, 2, 1, …
$ STAI_post_1_4 <dbl> NA, 3, 2, 1, …
$ STAI_post_1_5 <dbl> NA, 2, 2, 2, …
$ STAI_post_1_6 <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_1_7 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_1 <dbl> NA, 2, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_2_2 <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_3 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_2_4 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_2_5 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_6 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_2_7 <dbl> NA, 1, 1, 2, …
$ STAI_post_3_1 <dbl> NA, 2, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_3_2 <dbl> NA, 2, 3, 2, …
$ STAI_post_3_3 <dbl> NA, 3, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_3_4 <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 1, …
$ STAI_post_3_5 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 3, …
$ STAI_post_3_6 <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 2, …
$ moral_dilemma_dog <dbl> 9, 9, 8, 8, 3…
$ moral_dilemma_wallet <dbl> 9, 9, 7, 4, 9…
$ moral_dilemma_plane <dbl> 8, 9, 8, 8, 9…
$ moral_dilemma_resume <dbl> 7, 8, 5, 6, 5…
$ moral_dilemma_kitten <dbl> 9, 9, 8, 9, 5…
$ moral_dilemma_trolley <dbl> 5, 3, 5, 2, 4…
$ moral_dilemma_control <dbl> 9, 2, 9, 8, 8…
$ presentation_experience <dbl> NA, 2, 1, 2, …
$ presentation_unpleasant <dbl> NA, 63, 68, 3…
$ presentation_fun <dbl> NA, 58, 26, 5…
$ presentation_challenge <dbl> NA, 58, 65, 8…
$ PBC_1 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_2 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_3 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_4 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ PBC_5 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_1 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_2 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_3 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_4 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_5 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_6 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_7 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_8 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_9 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_10 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_11 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_12 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_13 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_14 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_15 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_16 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_17 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_18 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_19 <dbl> 1, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_20 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_21 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_22 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_23 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_24 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_25 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_26 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_27 <dbl> 5, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_28 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_29 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_30 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_31 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_32 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_33 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_34 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_35 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_36 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_37 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_38 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_39 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ REI_40 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_1 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_2 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_3 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_4 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_5 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_6 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_7 <dbl> 2, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_8 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_9 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_10 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_11 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_12 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_13 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_14 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_15 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_1_16 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_1 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_2 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_3 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_4 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_5 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_6 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_7 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_8 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_9 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_10 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_11 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_12 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_13 <dbl> 3, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_14 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_15 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_2_16 <dbl> 4, NA, NA, NA…
$ STAI_pre <dbl> 32, 49, 65, 4…
$ STAI_post <dbl> NA, 51, 41, 3…
$ MAIA_noticing <dbl> 14, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_not_distracting <dbl> 6, NA, NA, NA…
$ MAIA_not_worrying <dbl> 11, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_attention_regulation <dbl> 27, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_emotional_awareness <dbl> 20, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_self_regulation <dbl> 16, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_body_listening <dbl> 10, NA, NA, N…
$ MAIA_trusting <dbl> 12, NA, NA, N…
$ PBC <dbl> 21, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_rational_ability <dbl> 38, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_rational_engagement <dbl> 38, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_experiental_ability <dbl> 36, NA, NA, N…
$ REI_experiental_engagement <dbl> 39, NA, NA, N…
$ moral_judgment <dbl> 8.000000, 7.0…
$ moral_judgment_disgust <dbl> 8.666667, 9.0…
$ moral_judgment_non_disgust <dbl> 7.000000, 6.6…
$ presentation_evaluation <dbl> NA, 3, 3, 4, …
$ logbook <chr> NA, NA, NA, N…
$ exclude <dbl> 0, 0, 0, 0, 0…# A tibble: 188 × 42
STAI_pre_1_1 STAI_pre_1_2 STAI_pre_1_3
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2 1 2
2 3 2 3
3 4 3 3
4 2 2 2
5 1 1 1
6 2 2 1
7 2 2 1
8 1 1 1
9 2 2 1
10 4 2 3
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 39 more variables: STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_7 <dbl>, …Solution
# A tibble: 58 × 158
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
# ℹ 48 more rows
# ℹ 154 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>,
# mood_post <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …# A tibble: 188 × 158
subject STAI_pre start_date end_date finished
<dbl> <dbl> <date> <date> <dbl>
1 142 20 2014-06-11 2014-06-11 1
2 9 21 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1
3 162 22 2014-07-11 2014-07-11 1
4 39 23 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1
5 105 23 2014-05-11 2014-05-11 1
6 176 23 2014-07-11 2014-07-11 1
7 179 24 2014-07-11 2014-07-11 1
8 64 26 2014-04-11 2014-04-11 1
9 143 26 2014-06-11 2014-06-11 1
10 106 27 2014-05-11 2014-05-11 1
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 153 more variables: condition <chr>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>,
# mood_post <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …Transforming columns
Changing column names
rename(data, new_name = old_name)
to remember the order of appearance, consider = as “was”.
# A tibble: 188 × 158
start_date end_date done condition subject
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control 2
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 1
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 3
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 4
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control 7
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 6
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control 5
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control 9
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 16
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress 13
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 153 more variables: sex <chr>, age <dbl>,
# mood_pre <dbl>, mood_post <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>, …With a function: rename_with()
For the STAI columns convert names to lower case
# A tibble: 188 × 158
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 control
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 1 stress
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 154 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>,
# mood_post <dbl>, stai_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# stai_pre_1_2 <dbl>, stai_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# stai_pre_1_4 <dbl>, stai_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# stai_pre_1_6 <dbl>, stai_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …Adding columns: mutate()
Let’s create a new column mood_change that describes the change of the mood of the participant across the experiment.
- New column name:
mood_change - Computation: subtract
mood_prefrommood_post
# A tibble: 188 × 159
mood_pre mood_post mood_change start_date
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <date>
1 81 NA NA 2014-03-11
2 59 42 -17 2014-03-11
3 22 60 38 2014-03-11
4 53 68 15 2014-03-11
5 48 NA NA 2014-03-11
6 73 73 0 2014-03-11
7 NA NA NA 2014-03-11
8 100 NA NA 2014-03-11
9 67 74 7 2014-03-11
10 30 68 38 2014-03-11
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 155 more variables: end_date <date>,
# finished <dbl>, condition <chr>,
# subject <dbl>, gender <chr>, age <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, …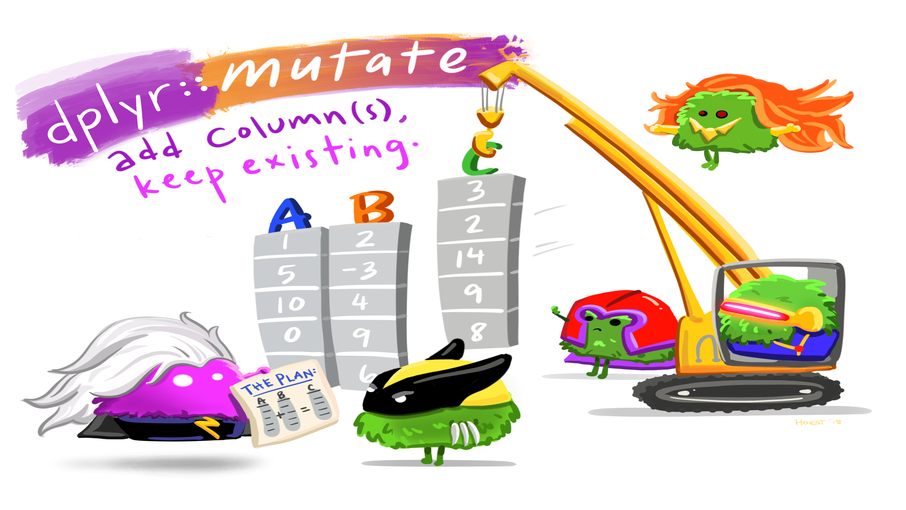
Within one mutate statement
Instant availability
Use new variables in the same function call right away!
judgments |>
mutate(
mood_change = mood_post - mood_pre,
# remove missing data before computation
mood_change_norm =
abs(mood_change / mean(mood_change, na.rm = TRUE))) |>
relocate(starts_with("mood")) |>
arrange(desc(mood_change_norm))# A tibble: 188 × 160
mood_pre mood_post mood_change mood_change_norm
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 66 0 -66 9.12
2 77 22 -55 7.60
3 47 100 53 7.32
4 25 72 47 6.49
5 22 69 47 6.49
6 37 83 46 6.36
7 20 62 42 5.80
8 60 100 40 5.53
9 22 60 38 5.25
10 30 68 38 5.25
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 156 more variables: start_date <date>,
# end_date <date>, finished <dbl>,
# condition <chr>, subject <dbl>, gender <chr>,
# age <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, …Replacing columns
Updating overwrites!
Using as names existing columns replaces their content.
Default column names
If not using names actions are used as names (avoid)
mutate() existing columns, centering mood columns
judgments |>
mutate(mood_pre = mood_pre / mean(mood_pre, na.rm = TRUE),
mood_post = mood_post / mean(mood_post, na.rm = TRUE),
mood_pre / mean(mood_post, na.rm = TRUE)) |>
select(starts_with("mood"))# A tibble: 188 × 3
mood_pre mood_post mood_pre/mean(mood_post, n…¹
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1.36 NA 1.36
2 0.994 0.680 0.994
3 0.371 0.971 0.371
4 0.893 1.10 0.893
5 0.809 NA 0.809
6 1.23 1.18 1.23
7 NA NA NA
8 1.68 NA 1.68
9 1.13 1.20 1.13
10 0.505 1.10 0.505
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ abbreviated name:
# ¹`mood_pre/mean(mood_post, na.rm = TRUE)`Vectorised if_else
Categorize values based on one condition.
TRUE/FALSE expression
Additionally: missing values can have its own category.
judgments |>
mutate(
mood_pre_cat = if_else(mood_pre < 25, "poor", "other", missing = "unknown")
) |>
select(mood_pre, mood_pre_cat)# A tibble: 188 × 2
mood_pre mood_pre_cat
<dbl> <chr>
1 81 other
2 59 other
3 22 poor
4 53 other
5 48 other
6 73 other
7 NA unknown
8 100 other
9 67 other
10 30 other
# ℹ 178 more rowsSwitch statements case_when() and case_match()
Categorize mood_pre. Tests come sequentially
judgments |>
mutate(mood_pre_cat = case_when(
mood_pre < 25 ~ "poor",
mood_pre < 50 ~ "mid",
mood_pre < 75 ~ "great",
mood_pre <= 100 ~ "exceptional",
.default = "missing data")) |>
select(mood_pre, mood_pre_cat) # A tibble: 188 × 2
mood_pre mood_pre_cat
<dbl> <chr>
1 81 exceptional
2 59 great
3 22 poor
4 53 great
5 48 mid
6 73 great
7 NA missing data
8 100 exceptional
9 67 great
10 30 mid
# ℹ 178 more rows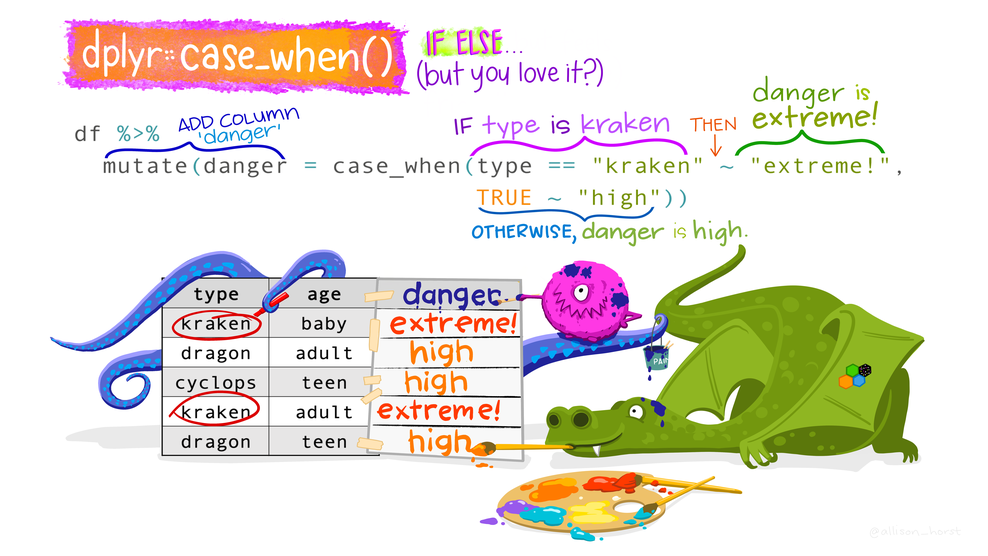
Note
The function if_else() provides a short hand for the case of a single condition only.
case_match() version
- The column is stated only once.
.defaultto control the unmatched values- New in
dplyr1.1.0
judgments |>
mutate(mood_pre_cat = case_match(
mood_pre,
c(0:24) ~ "poor",
c(25:49) ~ "mid",
c(50:74) ~ "great",
c(75:100) ~ "exceptional",
.default = "missing data")) |>
select(mood_pre, mood_pre_cat)# A tibble: 188 × 2
mood_pre mood_pre_cat
<dbl> <chr>
1 81 exceptional
2 59 great
3 22 poor
4 53 great
5 48 mid
6 73 great
7 NA missing data
8 100 exceptional
9 67 great
10 30 mid
# ℹ 178 more rowsAct on multiple columns at once using across()
Usage
Can be plugged into mutate(), summarise()…
across(ON WHO, DO WHAT)
- Columns selection:
- Argument
.cols tidyselecthelperseverything()= all columns.- Conditions (boolean) needs
where(),across(where(is.numeric))
- Argument
- Actions using functions:
- Argument
.fns fun, arg1, arg2\(x) fun(x), withplaceholderx- Multiple functions as arguments need to be wrapped up
- New column names can be controlled
- Argument
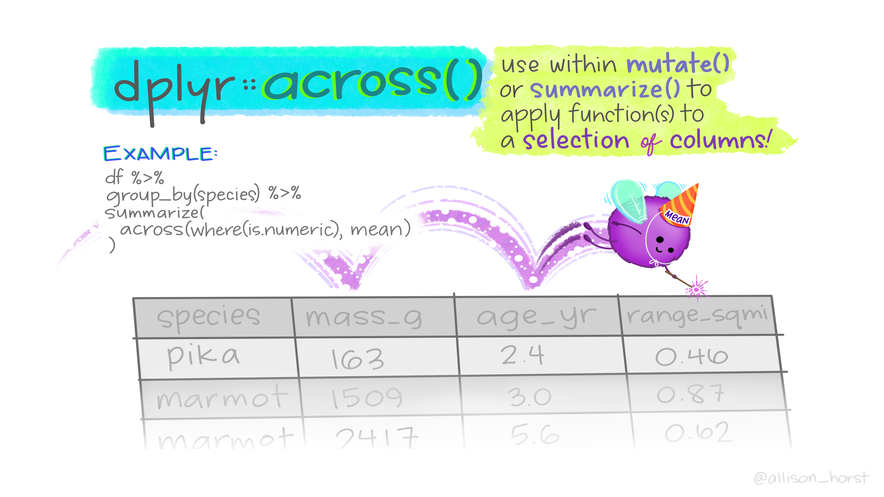
Examples of across() usage
Add 1 to the STAI questionnaire data
To convert Likert scales 0-4 to 1-5 (same column names)
# A tibble: 188 × 42
STAI_pre_1_1 STAI_pre_1_2 STAI_pre_1_3
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 3 2 3
2 4 3 4
3 5 4 4
4 3 3 3
5 2 2 2
6 3 3 2
7 3 3 2
8 2 2 2
9 3 3 2
10 5 3 4
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 39 more variables: STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_7 <dbl>, …To specify different names and not overwrite cols
judgments |>
mutate(across(starts_with("mood"), scale,
.names = "rescale_{.col}")) |>
select(contains("mood"))# A tibble: 188 × 4
mood_pre mood_post rescale_mood_pre[,1]
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 81 NA 1.17
2 59 42 -0.0193
3 22 60 -2.01
4 53 68 -0.343
5 48 NA -0.612
6 73 73 0.735
7 NA NA NA
8 100 NA 2.19
9 67 74 0.412
10 30 68 -1.58
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 1 more variable: rescale_mood_post <dbl[,1]>For filter the across is renamed to if any or all
Find rows where ANY of mood data columns are missing
Using lambdas
Reminder
\(x) x + 1 is just a shorthand for
function(x) {x + 1}
Add 1 to the STAI questionnaire data
# A tibble: 188 × 42
STAI_pre_1_1 STAI_pre_1_2 STAI_pre_1_3
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 3 2 3
2 4 3 4
3 5 4 4
4 3 3 3
5 2 2 2
6 3 3 2
7 3 3 2
8 2 2 2
9 3 3 2
10 5 3 4
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 39 more variables: STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_7 <dbl>, …Selecting columns with a predicate where()
Add 1 to numeric columns for all questionnaire data
- Predicate means return
TRUEorFALSE
# A tibble: 188 × 158
start_date end_date finished condition
<date> <date> <dbl> <chr>
1 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 control
2 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 stress
3 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 stress
4 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 stress
5 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 control
6 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 stress
7 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 control
8 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 control
9 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 stress
10 2014-03-11 2014-03-11 2 stress
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 154 more variables: subject <dbl>,
# gender <chr>, age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>,
# mood_post <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>, …Watch out
Now we also get subject changed!
More advanced across(): multiple functions
Summarise by the mean of mood
Better with naming and function arguments
summarise(judgments,
across(starts_with("moral_dil"),
list(aveg = \(x) mean(x, na.rm = TRUE),
sdev = \(x) sd(x, na.rm = TRUE)))) # A tibble: 1 × 14
moral_dilemma_dog_aveg moral_dilemma_dog_sdev
<dbl> <dbl>
1 7.35 2.17
# ℹ 12 more variables:
# moral_dilemma_wallet_aveg <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_wallet_sdev <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_plane_aveg <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_plane_sdev <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_resume_aveg <dbl>,
# moral_dilemma_resume_sdev <dbl>, …Manipulation by row - summing all scores
Tip
rowwise()- computation by rowc_across(ON WHO) - selects columns withtidyselectacross(ON WHO, DO WHAT)
judgments |>
mutate(total_stai =
sum(c_across(contains("STAI")),
na.rm = TRUE)) |>
select(subject, total_stai, contains("STAI"))# A tibble: 188 × 44
subject total_stai STAI_pre_1_1 STAI_pre_1_2
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2 22866 2 1
2 1 22866 3 2
3 3 22866 4 3
4 4 22866 2 2
5 7 22866 1 1
6 6 22866 2 2
7 5 22866 2 2
8 9 22866 1 1
9 16 22866 2 2
10 13 22866 4 2
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 40 more variables: STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl>, …judgments |>
rowwise() |>
mutate(total_stai = sum(c_across(
starts_with("STAI")), na.rm = TRUE)) |>
select(subject, total_stai, contains("STAI"))# A tibble: 188 × 44
# Rowwise:
subject total_stai STAI_pre_1_1 STAI_pre_1_2
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2 64 2 1
2 1 200 3 2
3 3 212 4 3
4 4 148 2 2
5 7 66 1 1
6 6 134 2 2
7 5 64 2 2
8 9 42 1 1
9 16 122 2 2
10 13 196 4 2
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 40 more variables: STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_7 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_2_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_2_6 <dbl>, …Your turn!
Exercises
Abbreviate the gender column such that only the first character remains.
Create a new
STAI_pre_categorycolumn. Usecase_match()to categorize values inSTAI_preas “low”, “normal” or “high”. For values < 25 inSTAI_preassign “low”, for values > 65 assign “high”, and for all other values assign “normal”. To easily see the new column, userelocate()to move it to the first position of the dataframe.Divide all entries in the REI questionnaire columns by 5, the maximal value, so the values will be between 0 and 1. Be careful with regular expression and leave out the REI summary columns!
Hint:across()allows modification of multiple columns in one go.Subset data to contain only subject and summary columns in the MAIA questionnaire. Keep only observations for subjects who filled in the MAIA questionnaire. How many of them are there?
Hint:Useif_all()orif_any()to filter across all columns.
15:00
Solution
judgments |>
mutate(STAI_pre_category = case_match(
STAI_pre,
c(0:24) ~ "low",
c(25:65) ~ "normal",
.default = "high")) |>
relocate(STAI_pre_category)# A tibble: 188 × 159
STAI_pre_category start_date end_date
<chr> <date> <date>
1 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
2 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
3 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
4 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
5 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
6 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
7 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
8 low 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
9 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
10 normal 2014-03-11 2014-03-11
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 156 more variables: finished <dbl>,
# condition <chr>, subject <dbl>, gender <chr>,
# age <dbl>, mood_pre <dbl>, mood_post <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_1 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_2 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_3 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_4 <dbl>,
# STAI_pre_1_5 <dbl>, STAI_pre_1_6 <dbl>, …Solution
# A tibble: 188 × 158
REI_1 REI_2 REI_3 REI_4 REI_5 REI_6 REI_7 REI_8
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 1 0.8 1 0.8 0.8 1 0.6 0.8
2 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
3 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
4 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
5 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.8 0.6 0.6 0.6
6 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
7 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.8 0.6 0.8
8 0.8 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
9 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
10 NA NA NA NA NA NA NA NA
# ℹ 178 more rows
# ℹ 150 more variables: REI_9 <dbl>,
# REI_10 <dbl>, REI_11 <dbl>, REI_12 <dbl>,
# REI_13 <dbl>, REI_14 <dbl>, REI_15 <dbl>,
# REI_16 <dbl>, REI_17 <dbl>, REI_18 <dbl>,
# REI_19 <dbl>, REI_20 <dbl>, REI_21 <dbl>,
# REI_22 <dbl>, REI_23 <dbl>, REI_24 <dbl>, …judgments |>
group_by(subject) |>
select( matches("MAIA_\\D")) |>
filter(!if_all(everything(), is.na)) # A tibble: 91 × 9
# Groups: subject [91]
subject MAIA_noticing MAIA_not_distracting
<dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
1 2 14 6
2 7 12 9
3 5 17 8
4 9 15 10
5 12 12 7
6 11 10 6
7 10 19 7
8 8 9 10
9 23 16 6
10 21 8 10
# ℹ 81 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: MAIA_not_worrying <dbl>,
# MAIA_attention_regulation <dbl>,
# MAIA_emotional_awareness <dbl>,
# MAIA_self_regulation <dbl>,
# MAIA_body_listening <dbl>,
# MAIA_trusting <dbl>Next up!
Grouping and summarising with dplyr
